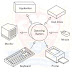
programming language
A vocabulary and set of grammatical rules for instructing a computer to perform specific tasks. The term programming language usually refers to high-level languages, such as BASIC, C, C++, COBOL, FORTRAN, Ada, and Pascal. Each language has a unique set of keywords (words that it understands) and a special syntax for organizing program instructions.High-level programming languages, while simple compared to human languages, are more complex than the languages the computer actually understands, called machine languages. Each different type of CPU has its own unique machine language.A programming language is typically divided into two elements: syntax and semantics. There is pretty much always a specification document to define both elements. For example, an ISO standard defines C, while Perl has a dominant implementation used as a reference.
 |
| Add caption |
An algorithm is described using the programming language. Programming languages are typically called computer languages; however, some authors deem programming languages to be subsets of computer languages. Since the oldest forms of programming languages like COBOL and FORTRAN, thousands of computer languages have been developed.
kinds of programing language
- computer science, computing - the branch of engineering science that studies (with the aid of computers) computable processes and structures
- artificial language - a language that is deliberately created for a specific purpose
- algorithmic language - an artificial language designed to express algorithms
- assembly language - a low-level programing language; close approximation to machine language
- computer language, computer-oriented language, machine language, machine-oriented language - a programming language designed for use on a specific class of computers
- multidimensional language - a programming language whose expressions are assembled in more than one dimension
- object language, target language - a computer language into which something written in another computer language is to be translated
- object-oriented programing language, object-oriented programming language - (computer science) a programming language that enables the programmer to associate a set of procedures with each type of data structure; "C++ is an object-oriented programming language that is an extension of C"
- one-dimensional language - a programming language whose expressions are represented by strings of characters
- stratified language - a language that cannot be used as its own metalanguage
- unstratified language - a programming language that (like natural language) can be used as its own metalanguage
- list-processing language, LISP - a flexible procedure-oriented programing language that manipulates symbols in the form of lists
- logic programing, logic programming, Prolog - a computer language designed in Europe to support natural language processing
- COBOL - common business-oriented language
- C - a general-purpose programing language closely associated with the UNIX operating system
- BASIC - a popular programming language that is relatively easy to learn; an acronym for beginner's all-purpose symbolic instruction code; no longer in general use
- Pascal - a programing language designed to teach programming through a top-down modular approach
Classifying Programming Languages